Research
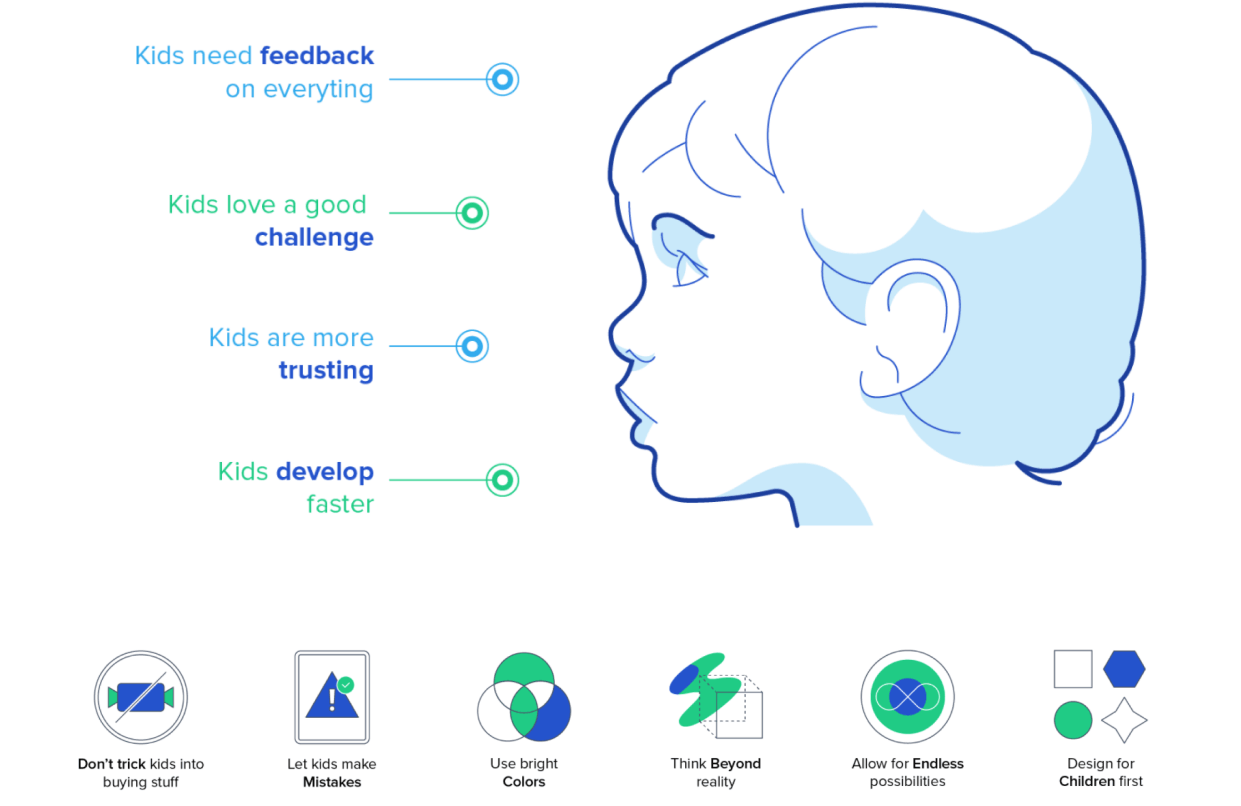
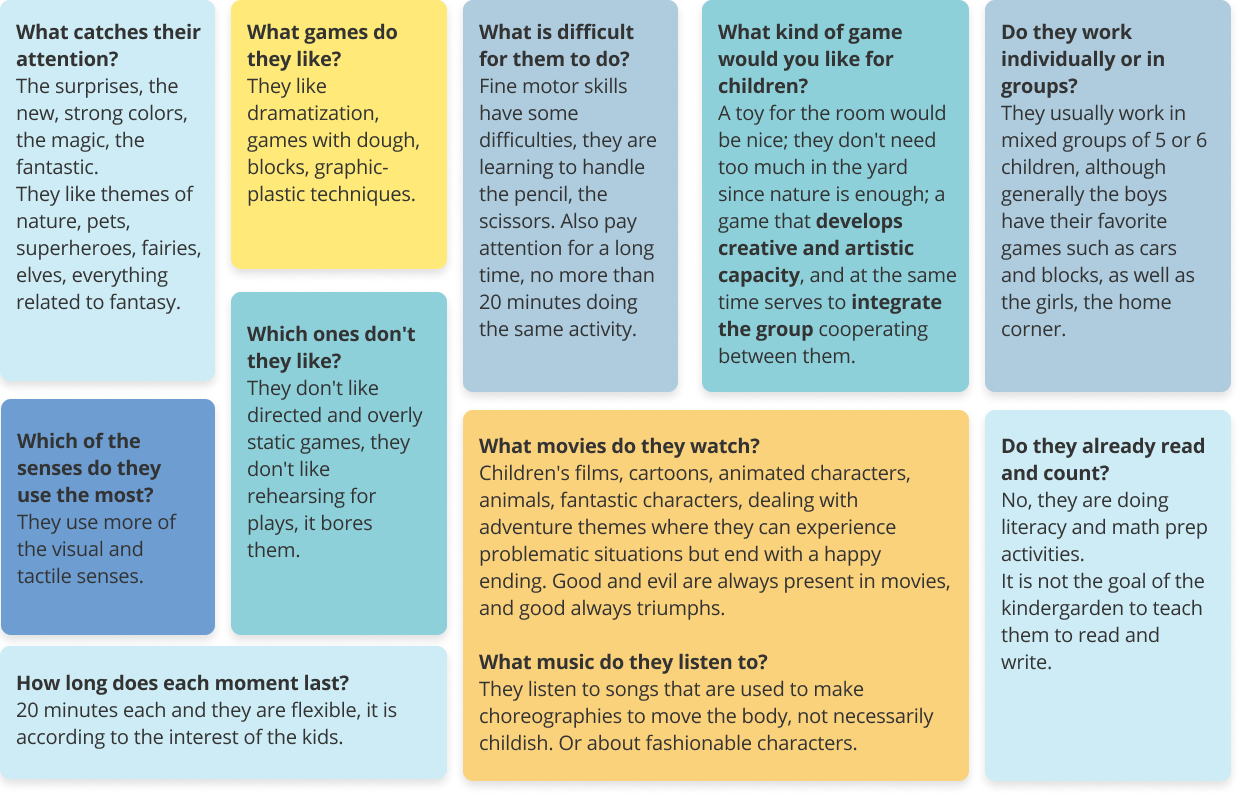
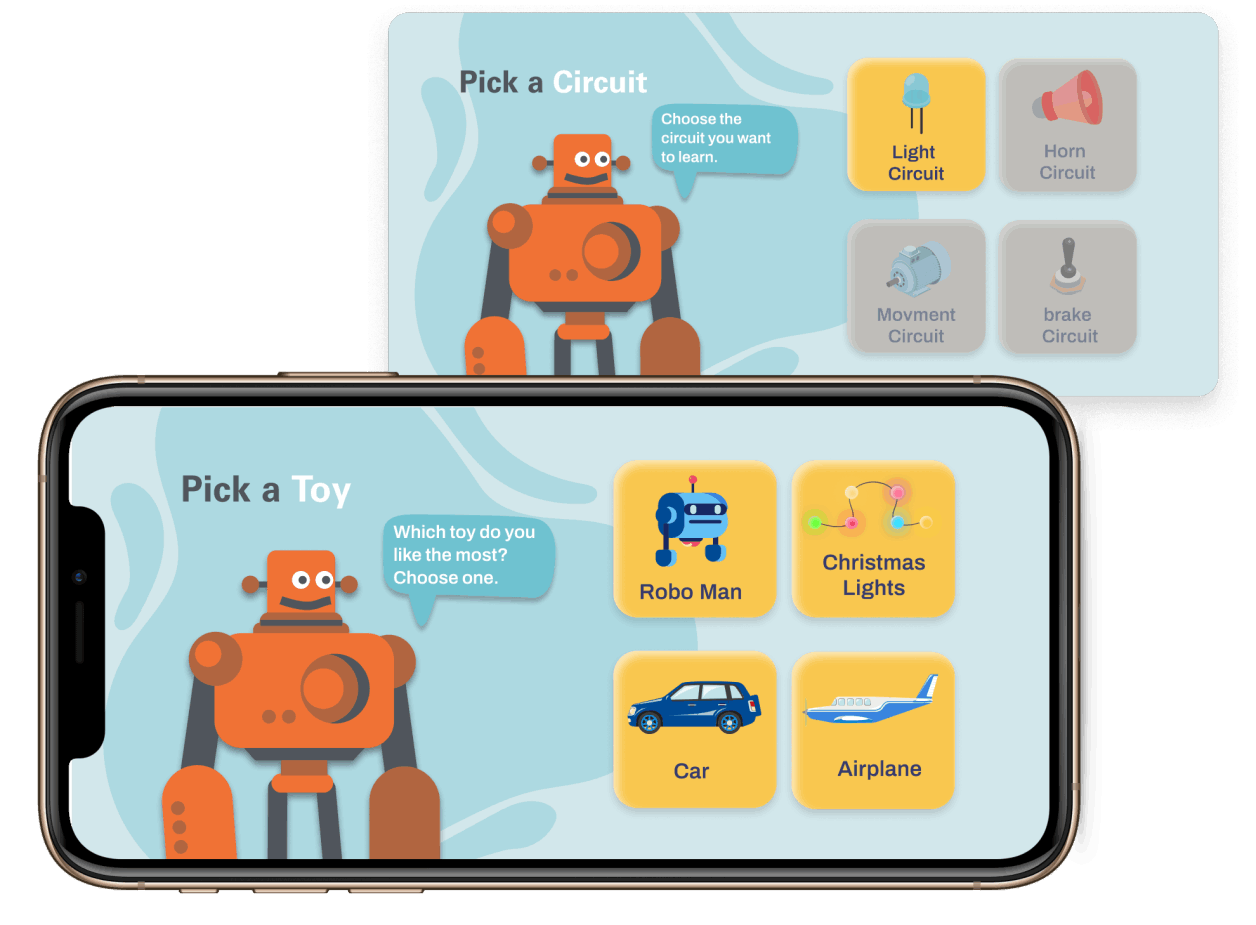
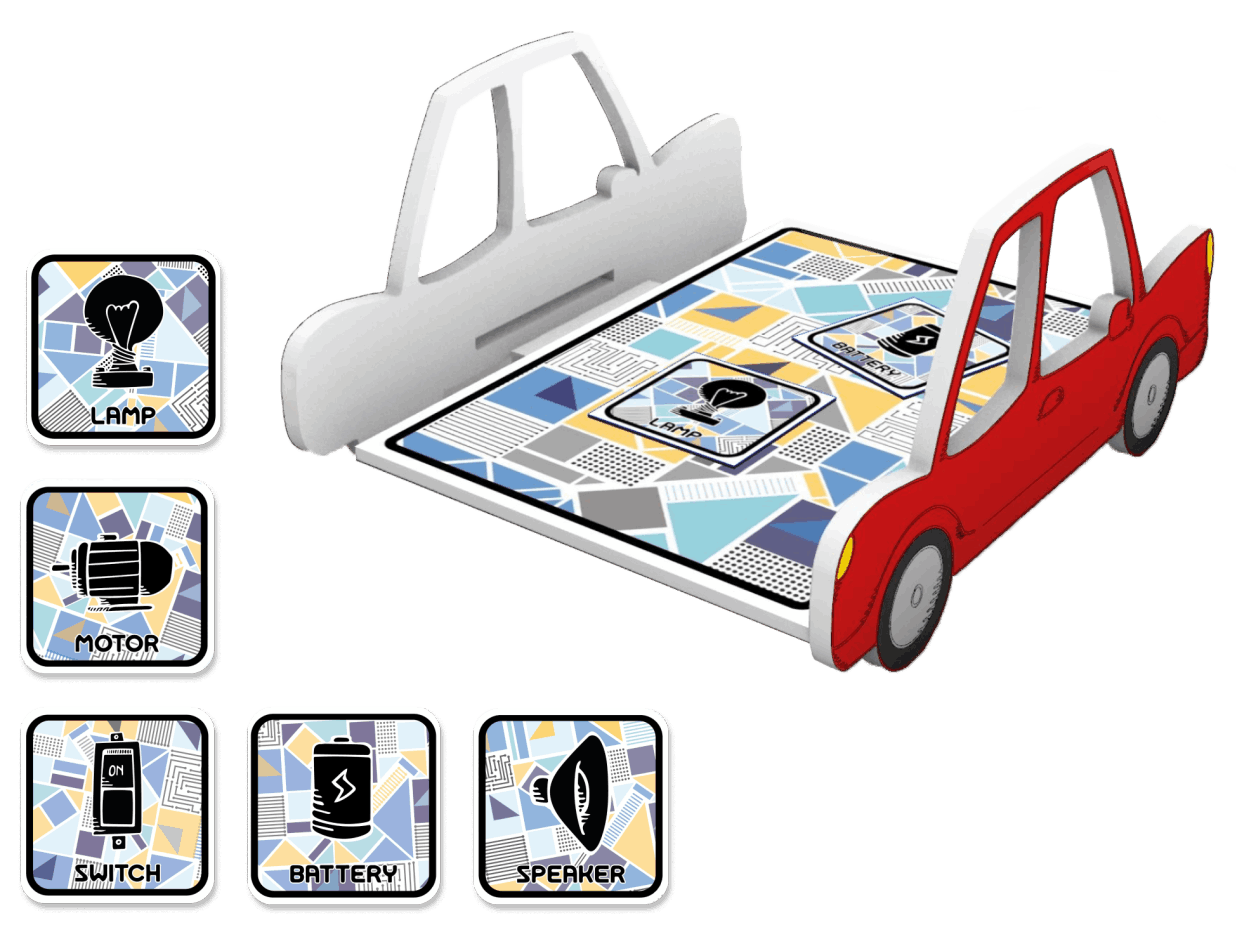
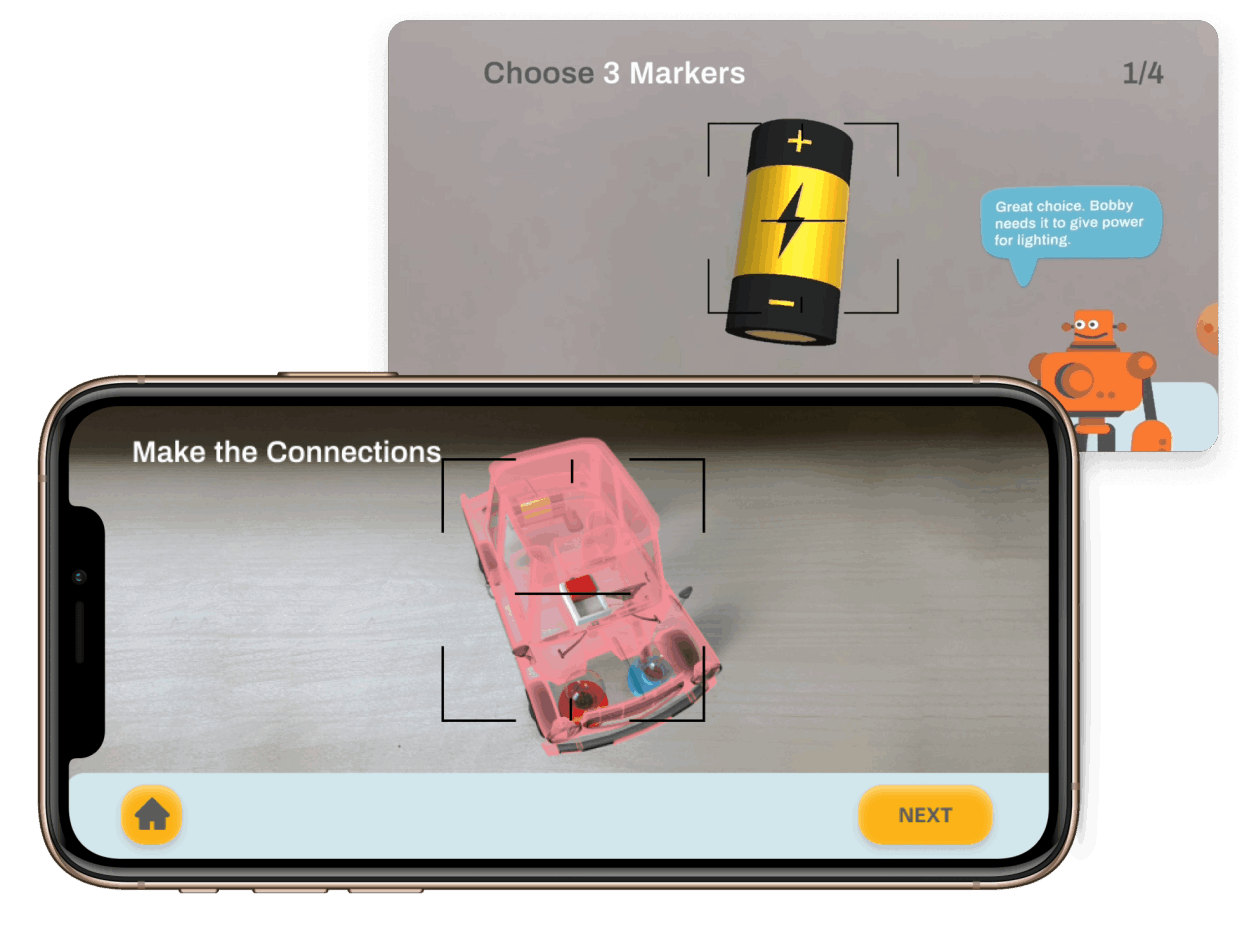
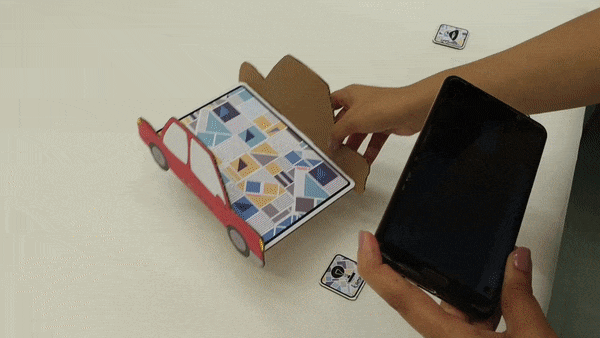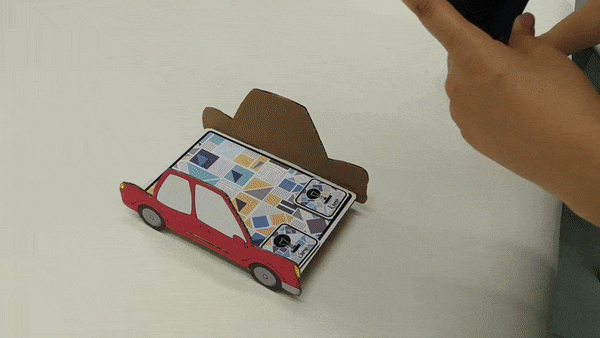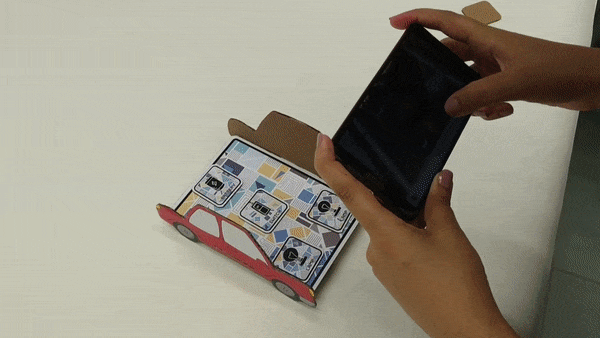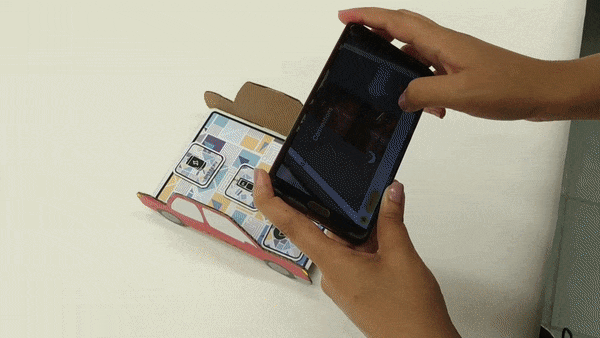
After selecting the topic, we did a research on electrical circuits, early childhood education, user interface for kids, and services that exist related to this area. We conducted an interview with a kindergarten teacher to learn about pedagogical aspects, educational dynamics, children's motivations, behaviors and interests. Finally a benchmark on existing solutions.
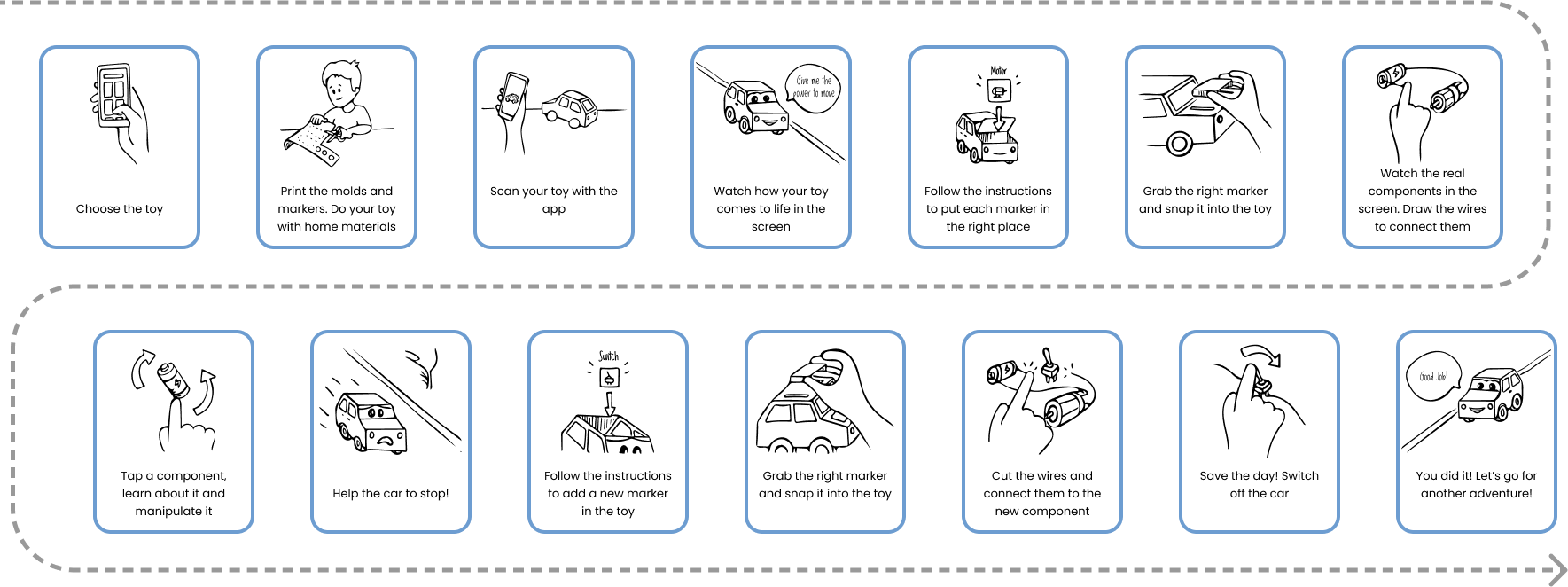
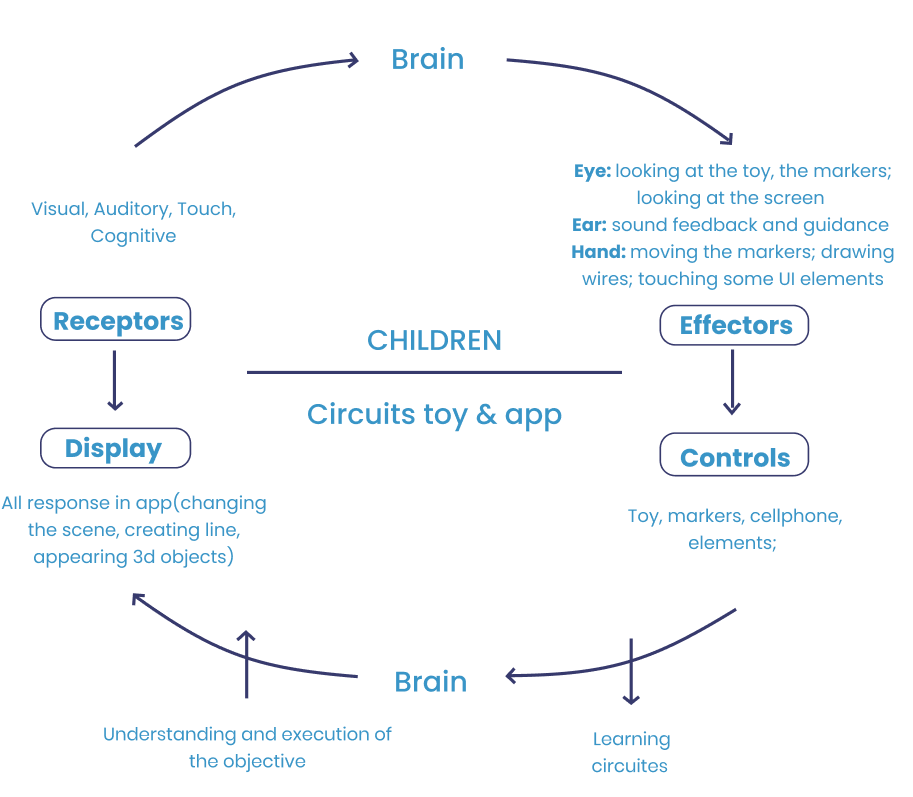
Arriving to define the different circuits to use, and rules and regulations for designing the digital platform for children.